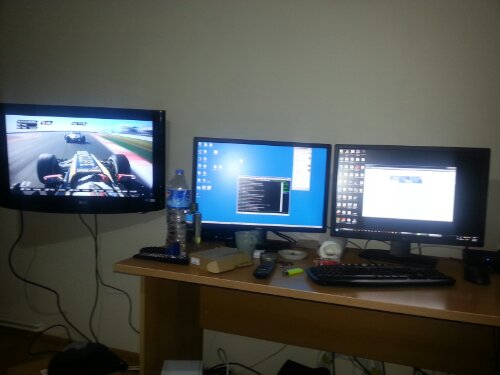
Bir kac gundur bu sistemle ugrasiyordum.
2 Monitor (Dell U2412M – 24″ IPS ekran ) + 1 Adet HD Ready LG 32″ TV
Hedef 3 unu extend ederek sistemi olusturmakti.
Sahip oldugum NVIDIA MSI GTX560TI TwinFrozer II OC edition kartimda NVIDIA nin kisitlamalari nedeni ile bunu yapamayinca ( NVIDIA tek GPU ile ayni anda sadece 2 cihaz calistirabilirsin diyor)
Kartimi AMD tarafinda Sapphire HD6950 2GB bir kart ile Takas etmek yoluna gittim
6950 Default ayarlarinda GTX560 TI kartimdan aziciak daha iyi sonuclar veren denk bir kart.
Yeni AMD kart geldikten sonra su konfigurasyon ile islemi tamamladim
Monitor 1 Mini Display Port ile karttan cikiyor Kartin kutusundan cikan adaptor ile normal Display Port oluyor ve baglaniyor
Monitor 2 Standart DVI kablosu ile Kartin DVI cikislarinin ust tarafindakine takili
TV Standart HDMI olarak bagli
Sonuc her 3 monitordu de extend edebiliyorum su an
Bir yanda Tv + 2 Monitor
Guzel ve arzu ettigim bir setup oldu 🙂
NOT: 6950 Geldikten sonra bu kartin cok basit bir BIOS upgradei ile 6970 Olarak calistirilabildiginide farkettim.
Gerekli bilgi asagidaki linklerde var:
Bana Daha cok hiz veya 6970 Lazim olmadigindan su an islemi yapmiyorum. Ama belki ilerde yaparim bende 6950@6970 olayini.
http://www.techpowerup.com/articles/overclocking/vidcard/159
http://www.legitreviews.com/article/1608/5/
http://blog.daum.net/victorys/11153513

